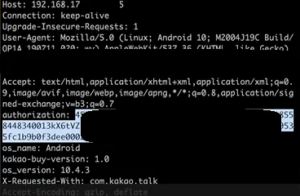
The demand for cybersecurity professionals is growing rapidly as organizations seek to protect their digital assets from an increasing array of threats. Here’s a look at some of the top cybersecurity job roles and a guide on how to secure these positions.
1. Security Analyst
Role: Security analysts monitor and protect an organization’s computer networks and systems. They are responsible for identifying vulnerabilities, implementing security measures, and responding to incidents.
How to Get There:
- Education: Obtain a degree in computer science, information technology, or cybersecurity.
- Certifications: Earn certifications such as CompTIA Security+, Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), and Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH).
- Skills: Develop strong analytical, problem-solving, and communication skills. Gain experience with security tools and technologies.
- Experience: Start with internships or entry-level positions in IT or security. Gain hands-on experience through labs and simulations.
2. Penetration Tester (Ethical Hacker)
Role: Penetration testers simulate cyber attacks to identify and exploit vulnerabilities in systems, networks, and applications. They provide recommendations to improve security defenses.
How to Get There:
- Education: A degree in computer science or cybersecurity is beneficial.
- Certifications: Obtain certifications like CEH, Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP), and Certified Penetration Testing Engineer (CPTE).
- Skills: Strong knowledge of networking, programming, and security tools. Proficiency in scripting languages like Python and familiarity with penetration testing frameworks.
- Experience: Build a portfolio of penetration testing projects. Participate in Capture The Flag (CTF) competitions and bug bounty programs.
3. Security Architect
Role: Security architects design and implement secure network solutions that protect against cyber threats. They develop security policies, procedures, and best practices.
How to Get There:
- Education: A degree in computer science, information security, or a related field.
- Certifications: CISSP, Certified Information Security Manager (CISM), and TOGAF certification for enterprise architecture.
- Skills: Expertise in security protocols, encryption, and firewall management. Strong understanding of risk management and threat modeling.
- Experience: Several years of experience in IT security roles. A background in network architecture or system administration is beneficial.
4. Incident Responder
Role: Incident responders are the first line of defense when a security breach occurs. They analyze, contain, and mitigate security incidents, and develop strategies to prevent future incidents.
How to Get There:
- Education: A degree in cybersecurity, information technology, or a related field.
- Certifications: Certified Incident Handler (GCIH), CISSP, and Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA).
- Skills: Strong analytical and problem-solving skills. Ability to work under pressure and knowledge of incident response frameworks.
- Experience: Experience in security operations centers (SOCs) or as a security analyst. Hands-on experience with incident response tools and methodologies.
5. Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)
Role: The CISO is responsible for overseeing the organization’s cybersecurity strategy and ensuring that information assets are protected. They lead security teams and work closely with executive management.
How to Get There:
- Education: A degree in computer science, information security, business administration, or a related field. An MBA can be beneficial.
- Certifications: CISM, CISSP, Certified Information Security Executive (CISE).
- Skills: Leadership, strategic planning, and risk management skills. In-depth knowledge of cybersecurity frameworks and regulatory requirements.
- Experience: Extensive experience in cybersecurity management roles. Proven track record of developing and implementing security strategies.
6. Security Consultant
Role: Security consultants provide expert advice to organizations on how to protect their digital assets. They conduct security assessments, develop security policies, and recommend solutions.
How to Get There:
- Education: A degree in computer science, information technology, or cybersecurity.
- Certifications: CISSP, CEH, Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA), and Certified Information Security Manager (CISM).
- Skills: Strong analytical, problem-solving, and communication skills. Ability to assess security risks and recommend effective solutions.
- Experience: Experience in various cybersecurity roles. A background in IT consulting can be advantageous.
7. Security Software Developer
Role: Security software developers design and implement security features within software applications. They ensure that applications are secure from the ground up.
How to Get There:
- Education: A degree in computer science or software engineering.
- Certifications: Secure Software Practitioner (CSSLP) and Offensive Security Certified Expert (OSCE).
- Skills: Proficiency in programming languages such as Java, C++, Python. Strong understanding of secure coding practices and software development life cycle (SDLC).
- Experience: Experience in software development and an understanding of cybersecurity principles. Participation in open-source security projects can be beneficial.
8. Cyber Range for Upskilling Your Cybersecurity Knowledge
1. Hands-On Learning: Cyber ranges provide a realistic, hands-on environment where you can practice and hone your cybersecurity skills.
2. Real-World Scenarios: They simulate real-world cyber threats and attacks, helping you learn how to respond effectively.
3. Skill Validation: Using a cyber range, you can demonstrate and validate your skills to potential employers, showcasing your practical expertise.
4. Career Advancement: By upskilling through a cyber range, you can increase your chances of landing a cybersecurity job and advancing your career.
To know more, click here
Conclusion The field of cybersecurity offers a wide range of career opportunities, each requiring a unique set of skills and qualifications. By pursuing relevant education, certifications, and practical experience, aspiring cybersecurity professionals can position themselves for success in these high-demand roles. At PurpleSynapz, we are dedicated to providing the training and resources needed to help you achieve your career goals in cybersecurity.
Views: 62